Toyota Camry Cvt: Unlocking Fuel Efficiency, Performance, And Seamless Driving
Toyota’s Camry CVT is an advanced transmission offering a seamless driving experience, fuel efficiency, and performance benefits. Its flexible pulley system and continuous gear ratio allow it to adapt to varying driving conditions, maintaining optimal engine power. The CVT eliminates abrupt gear changes, resulting in smooth acceleration and a more refined ride. While durability and maintenance considerations may exist compared to traditional transmissions, the Camry’s CVT offers a compelling balance of fuel efficiency, performance, and driving enjoyment.
Understanding CVT Transmissions in the Toyota Camry
Prepare yourself to embark on a thrilling journey into the world of Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs). These remarkable transmissions have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering unparalleled benefits that traditional transmissions simply cannot match. Today, we’ll delve into the inner workings of CVT transmissions, using the Toyota Camry as our shining example.
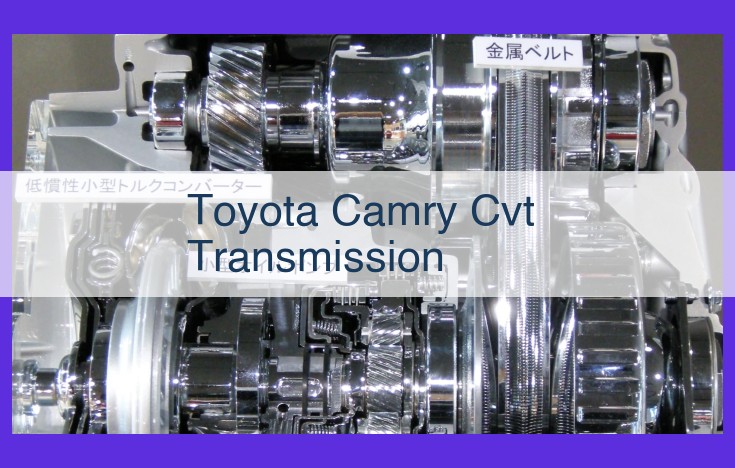
CVTs boast an ingenious design that sets them apart from their conventional counterparts. At the heart of this transmission lies a variable-diameter pulley system. As the engine’s speed changes, these pulleys adjust their diameters, ensuring optimal gear ratios for every driving condition. A specially engineered belt connects the pulleys, transmitting power smoothly and efficiently.
The transmission fluid plays a pivotal role in CVT operation. It lubricates vital components, cools the system, and transmits hydraulic pressure to control the pulley movements. This intricate interplay ensures that the Camry’s CVT operates with exceptional precision and reliability.
The Pulley System, Belt, and Transmission Fluid: The Heart of a CVT Transmission
The continuously variable transmission (CVT) in the Toyota Camry employs a unique pulley system that sets it apart from traditional transmissions. At its core are two pulleys, one connected to the engine and the other to the wheels. These pulleys are named the drive pulley and the driven pulley, respectively.
The special feature of these pulleys is their variable diameters. They can change their size to create an infinite range of gear ratios, allowing the transmission to seamlessly adapt to driving conditions. As the drive pulley reduces in diameter, the driven pulley expands, and vice versa. This variation maintains the optimal engine power band, delivering smooth and efficient performance.
Connecting these pulleys is a flexible belt made of strong materials to withstand the varying forces. It wraps around the pulleys and transmits power between them. The belt’s design ensures that it maintains contact with the pulleys in all positions, eliminating slip and maximizing power transfer.
To ensure smooth operation, the system relies on transmission fluid. This fluid acts as a lubricant, reducing friction between the belt and pulleys. It also helps dissipate heat generated by the transmission process, preventing overheating and maintaining optimal performance. The fluid’s viscosity is carefully formulated to ensure both lubrication and cooling efficiency.
Torque Converter and Final Drive: The Powerhouses of the CVT
The torque converter in a CVT transmission plays a pivotal role in transmitting torque from the engine to the transmission. This component is a fluid coupling that allows the engine to run independently of the transmission, providing a seamless and smooth transition when shifting gears.
The torque converter consists of three main elements: an impeller, a turbine, and a stator. The impeller is connected to the engine and rotates with it. The turbine is connected to the transmission and rotates in response to the impeller’s motion. The stator is positioned between the impeller and the turbine and helps to redirect the flow of fluid for increased torque multiplication.
After the torque converter, the power is transferred to the final drive. The final drive is a set of gears that reduces the speed of the transmission output and increases the torque. The final drive is typically composed of a ring gear and a pinion gear. The ring gear is connected to the transmission output, and the pinion gear is connected to the driveshaft.
The Role of the Final Drive
The final drive serves several crucial functions. It:
- Reduces the speed of the transmission output to match the speed required by the wheels.
- Increases the torque to provide the necessary force for driving the vehicle.
- Reverses the direction of the transmission output to rotate the wheels in the desired direction.
In summary, the torque converter and final drive are essential components of a CVT transmission. The torque converter transmits torque from the engine to the transmission, while the final drive reduces the speed and increases the torque, providing the power necessary for vehicle propulsion.
Gear Ratio and Fuel Efficiency: The CVT’s Secret Weapon
Imagine driving a car that adapts to your every need, seamlessly shifting through an infinite number of gears to deliver optimal performance and efficiency. This is the beauty of a Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT). Unlike traditional transmissions with fixed gear ratios, CVTs provide a continuous range of ratios, allowing for the perfect balance between acceleration, power, and fuel savings.
The key to this flexibility lies in the CVT’s unique pulley system. Two pulleys, each with variable diameters, are connected by a belt. As the pulleys expand or contract, the belt adjusts its position, effectively changing the gear ratio. This ingenious design allows the CVT to seamlessly adjust to the engine’s power output, delivering the most suitable gear ratio for any driving condition.
The continuous gear ratio of a CVT has a profound impact on fuel efficiency. Traditional transmissions often operate at either too high or too low of a gear ratio for optimal fuel consumption. However, CVTs can maintain the engine in its most efficient power band, where it burns less fuel to produce the same amount of power. This optimized engine operation results in significant fuel savings.
Here’s a simple analogy to illustrate the CVT’s advantage:
Imagine a runner who wants to maintain a constant speed. A traditional transmission would be like giving the runner a fixed gear bike. The runner would have to gear up or down periodically to adjust to uphill or downhill slopes. However, with a CVT, the runner would have a bike with an infinitely adjustable gear ratio. They could smoothly accelerate up hills without overexerting themselves, and coast down slopes without losing momentum. This is the power of the CVT’s continuous gear ratio, optimizing fuel efficiency by keeping the engine in its sweet spot.
Smooth Shifting
- Discussion of the CVT’s seamless shifting, elimination of abrupt gear changes, and its contribution to a smoother driving experience.
Smooth Sailing: The Secret to a Seamless Driving Experience
In the realm of driving, few things are more disconcerting than the jolt of abrupt gear changes. This is where Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) shine brightest. Unlike traditional transmissions that rely on fixed gears, CVTs boast a seamless shifting experience, eliminating all traces of jarring transitions.
Imagine cruising down the open road with a Camry equipped with a CVT. Instead of the familiar lurches and hesitations associated with conventional transmissions, you’ll encounter an unparalleled smoothness. The transmission effortlessly adjusts to the changing demands of the road, maintaining an optimal engine speed that maximizes efficiency and power.
The secret lies in the CVT’s ingenious design. It employs two variable-diameter pulleys connected by a flexible belt. As the pulleys adjust their diameters, the belt changes its length accordingly, creating an infinite number of gear ratios. This continuous variation ensures that the engine is always operating within its sweet spot, delivering a buttery-smooth ride.
Gone are the days of jerky gear changes that interrupt the flow of your driving. With a CVT, you can expect a graceful transition through the entire rev range, akin to a gentle wave gliding through the ocean. This seamlessness not only enhances your driving pleasure but also reduces wear and tear on your vehicle’s powertrain, promoting longevity and reliability.
Acceleration: Unlocking Optimal Power with CVTs
In the world of transmissions, CVTs (Continuously Variable Transmissions) stand out as masters of acceleration. Unlike traditional transmissions with their fixed gear ratios, CVTs continuously adjust their gear ratios to maintain optimal engine power bands. This means your car always operates at its most efficient and responsive.
The CVT’s secret lies in its unique pulley system, which allows for infinitely variable gear ratios. As you accelerate, the CVT seamlessly adjusts the diameters of its pulleys, keeping the engine within its sweet spot. This constant adjustment ensures maximum power is delivered to the wheels, resulting in smoother and more efficient acceleration.
Imagine yourself behind the wheel of a Toyota Camry equipped with a CVT. As you press on the gas pedal, the CVT instantaneously finds the ideal gear ratio, minimizing power loss and maximizing torque. You feel a surge of acceleration as your Camry responds with effortless speed. It’s like having a race-tuned transmission in your everyday car, providing you with exhilarating performance whenever you need it.
CVTs not only enhance acceleration but also contribute to better fuel efficiency. By maintaining optimal engine speed, the CVT reduces unnecessary fuel consumption and maximizes the car’s mileage. It’s a win-win situation for both performance and the environment.
Durability and Cost: CVT vs Traditional Transmissions
In the world of automotive engineering, the debate between Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) and traditional transmissions has long persisted. While CVTs offer compelling advantages in terms of fuel efficiency and smooth shifting, questions linger about their durability and cost implications.
Durability
CVTs and traditional transmissions differ in their longevity and maintenance requirements. Traditional transmissions, characterized by fixed gear ratios, are generally regarded as more robust. However, with advancements in materials and design, CVTs have made significant strides in durability. Proper maintenance, such as regular fluid changes, is crucial for both types of transmissions.
Cost
The initial cost of a CVT is typically higher than that of a traditional transmission. However, it’s worth considering the potential savings in fuel consumption over time. CVTs optimize engine performance, resulting in better gas mileage. Additionally, regular maintenance intervals for CVTs are generally on par with traditional transmissions, mitigating any significant cost differences in the long run.
Repairs
Transmissions, whether traditional or CVT, can require repairs over their lifetime. While CVTs may have some unique maintenance needs, such as belt or pulley replacements, it’s important to remember that repairs for traditional transmissions can be equally expensive. The complexity of modern transmissions, regardless of type, has increased the cost of repairs in recent years.
Ultimately, the choice between a CVT and a traditional transmission should consider individual driving habits and priorities. If fuel efficiency and a smooth driving experience are paramount, a CVT offers compelling benefits. However, if durability and initial cost are deciding factors, a traditional transmission may be more suitable.