Maximize Adblue Lifespan: Essential Storage Practices For Diesel Engine Performance
AdBlue, or diesel exhaust fluid, extends the lifespan of vehicles with diesel engines by reducing nitrogen oxide emissions. Proper storage and handling are crucial for its effectiveness. AdBlue lifespan is influenced by temperature, light exposure, and contaminants. Ideal storage conditions minimize degradation and freezing, ensuring optimal performance. Regular usage prevents excessive storage and improves AdBlue quality. By adhering to recommended storage practices and using high-quality products, you can maximize AdBlue lifespan and enhance vehicle performance.
AdBlue: The Secret to Cleaner Diesel Emissions
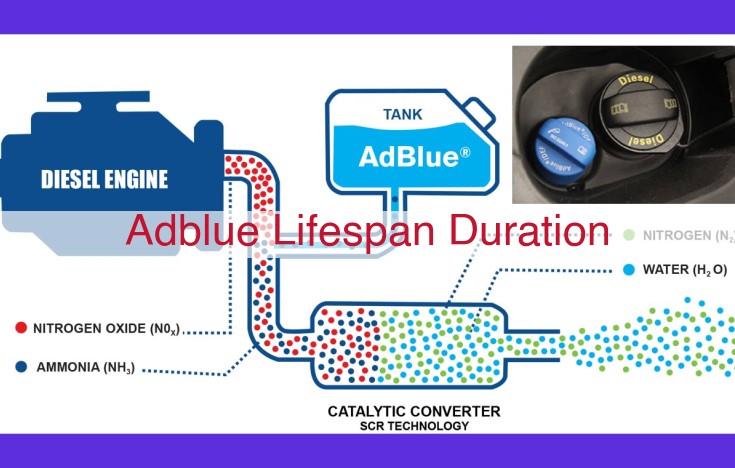
In today’s world, environmental consciousness takes center stage. AdBlue, a revolutionary fluid, plays a pivotal role in reducing harmful nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions from diesel engines, contributing significantly to cleaner air and a healthier planet.
AdBlue is a colorless liquid composed of high-purity urea and deionized water. It’s stored in a dedicated tank in vehicles with diesel engines and injected into the exhaust system upstream of the Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) unit.
Upon entering the exhaust stream, AdBlue undergoes a chemical reaction, transforming NOx into harmless nitrogen and water vapor. This remarkable process effectively reduces NOx emissions, helping diesel vehicles meet stringent emissions standards and safeguarding the environment from the harmful effects of these pollutants.
Factors Influencing AdBlue Consumption
The amount of AdBlue your vehicle consumes depends on a variety of factors, including:
- Fuel Consumption: The more fuel your vehicle burns, the more AdBlue it will need. This is because AdBlue is used to treat the nitrogen oxides (NOx) produced by diesel combustion. The higher the NOx output, the more AdBlue will be required.
- Driving Conditions: Stop-and-go traffic and heavy loads can also increase AdBlue consumption. This is because these conditions lead to higher NOx production.
Typical Tank Capacity
The typical AdBlue tank capacity for vehicles with diesel engines ranges from 15 to 25 liters. This capacity is designed to provide a sufficient range between fill-ups. However, the actual range you can expect will vary depending on the factors mentioned above.
For example, a vehicle that primarily travels on highways will likely have a longer AdBlue range than a vehicle that is frequently driven in stop-and-go traffic. Similarly, vehicles towing heavy loads will also have a shorter _AdBlue range._
It is important to check your vehicle’s _AdBlue level regularly and fill up the tank as needed. Running out of AdBlue can damage your vehicle’s catalytic converter, leading to costly repairs._
Describe the ideal storage conditions (temperature, light exposure, humidity) for AdBlue and the impact of product quality on its lifespan.
AdBlue Storage: Ensuring Optimal Lifespan
AdBlue, the indispensable diesel exhaust fluid, requires careful storage to maintain its effectiveness. Its stability and longevity are directly influenced by environmental factors.
Ideal Storage Conditions
Store AdBlue in a cool (ideally between 0-25°C), dry place protected from direct sunlight. Exposure to extreme temperatures, especially prolonged, can degrade the fluid and shorten its lifespan by accelerating chemical reactions. When temperatures rise above 30°C, the degradation process intensifies.
Humidity is another crucial consideration. Exposure to excessive moisture can cause AdBlue to absorb water, leading to a decrease in its concentration. This compromised fluid may not perform as effectively in reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions, diminishing its environmental benefits.
Impact of Product Quality
The purity of AdBlue plays a pivotal role in its storage life. High-quality products meet stringent ISO standards, ensuring a consistent composition. Impurities and contaminants can compromise AdBlue’s stability, exacerbating degradation and potentially causing clogging in the injection system.
Prolonging AdBlue Lifespan
Adhering to recommended storage guidelines and using high-quality AdBlue are essential for extending its lifespan. Additionally, regular usage can reduce the fluid’s exposure to storage conditions that promote degradation. Every journey, no matter how short, helps refresh the AdBlue in the vehicle’s tank and minimizes its time spent in storage.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure your AdBlue storage practices contribute to optimal engine performance and environmental protection.
AdBlue Degradation and the Importance of Purity
Just like the fragile petals of a delicate flower wither under the harsh glare of the sun, AdBlue, the lifeblood of diesel exhaust systems, can degrade and lose its potency over time. The cruel effects of temperature fluctuations and the insidious presence of contaminants are the primary culprits behind this unfortunate demise.
Temperature plays a pivotal role in the lifespan of AdBlue. Extreme heat, like the scorching breath of a desert wind, accelerates the degradation process. At temperatures above its optimal range, AdBlue begins to break down, losing its urea content and diminishing its effectiveness. Conversely, freezing temperatures can also pose a threat to AdBlue’s integrity. When the mercury dips below its freezing point, AdBlue may crystallize, rendering it unusable and potentially damaging to the vehicle’s systems.
Just as a pure, unsullied stream becomes polluted by foreign elements, AdBlue’s efficacy can be compromised by contaminants. These unwelcome intruders, such as oil, fuel, or other chemicals, can disrupt AdBlue’s delicate balance and hinder its ability to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions. Even seemingly insignificant traces of these contaminants can have detrimental effects, so maintaining the purity of AdBlue is paramount to ensuring its optimal performance.
AdBlue Degradation and Freezing
The Freezing Point of AdBlue
As the temperatures drop, it’s crucial to understand how AdBlue reacts to extreme cold. AdBlue’s freezing point is approximately -11°C (12°F), meaning it can solidify and become unusable if exposed to such conditions.
Considerations for Cold Weather Operation
To ensure optimal performance during cold weather, it’s essential to store AdBlue in heated or insulated tanks, and to avoid overfilling the tank. When the temperature dips below freezing, AdBlue may crystallize and clog the system, leading to engine performance issues.
Additionally, using high-quality AdBlue that meets ISO standards is particularly important in cold weather conditions. Impurities or contaminants can lower the freezing point of AdBlue and affect its performance.
Signs of Degradation and Troubleshooting
If AdBlue is exposed to extreme cold or otherwise compromised, it may exhibit signs of degradation. The color may change to a darker hue, and an unpleasant odor may become noticeable. These indicators suggest that the AdBlue has degraded and needs to be replaced.
In the event of suspected AdBlue degradation, it’s essential to resolve the issue promptly. Driving with degraded AdBlue can damage the engine and exhaust system. Troubleshooting steps include:
- Checking the AdBlue tank for any signs of physical damage or contamination.
- Replacing the AdBlue with a fresh, high-quality solution.
- Checking the engine and exhaust system for any related issues.
The Significance of Purity and Concentration for AdBlue Performance
AdBlue: The Essential Ingredient for Emissions Control
AdBlue, a remarkable solution of urea and water, plays a crucial role in reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions from diesel engines. This game-changing fluid transforms harmful NOx gases into harmless nitrogen and water, ensuring cleaner air for our communities and a healthier future for our planet.
Purity Matters: The Key to Unlocking AdBlue’s Potential
Just like the human body, AdBlue requires purity to function effectively. Impurities in the solution can disrupt its delicate chemical composition, hindering its ability to break down NOx emissions. Hence, it’s critical to use high-quality AdBlue from reputable sources that adhere to stringent industry standards.
Concentration: The Balancing Act of Efficiency and Durability
The concentration of urea in AdBlue is another vital factor. Too low a concentration may compromise its effectiveness in reducing NOx emissions, while too high a concentration can lead to crystallization and blockages in the AdBlue system. Therefore, strict adherence to the recommended urea concentration is essential for optimal performance and long-lasting durability.
Consequences of Substandard AdBlue: A Cautionary Tale
Using substandard AdBlue can have dire consequences. Impurities can cause nozzle and injector clogging, leading to costly repairs or even engine damage. Moreover, low-quality AdBlue may contain contaminants that degrade the solution over time, reducing its effectiveness and potentially voiding manufacturer warranties.
Safeguarding AdBlue’s Integrity: A Call to Action
Protecting the purity and concentration of AdBlue is not just a technicality; it’s an investment in our environment and our vehicles. By using high-quality AdBlue and adhering to recommended storage and handling practices, we can ensure its optimal performance for years to come.
Remember, AdBlue is the lifeline of diesel emissions control. Let’s treat it with the care and attention it deserves to keep our engines running smoothly and our air clean for generations to come.
AdBlue Quality and Standards
To ensure optimal performance, AdBlue must meet strict quality standards. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has established several norms that AdBlue manufacturers must comply with.
One crucial standard is ISO 22241, which specifies the purity and concentration requirements for AdBlue. It sets limits on contaminants, such as urea, chlorides, and heavy metals, which can impair the efficiency of AdBlue.
Moreover, ISO 18611-1 defines the production, storage, and handling requirements for AdBlue. This standard ensures that AdBlue is stored and dispensed in a way that preserves its quality.
Manufacturers also conduct regular testing to ensure that their AdBlue products meet these standards. They analyze samples for concentration, impurities, and degradation to guarantee consistent quality. This rigorous testing helps prevent the distribution of substandard AdBlue that could compromise engine performance.
By adhering to ISO standards and implementing regular testing, manufacturers play a vital role in ensuring the quality and reliability of AdBlue. This protects your vehicle, reduces emissions, and ultimately contributes to a more sustainable environment.
AdBlue: Extending the Lifespan of Your Diesel Engine’s Ally
AdBlue, also known as diesel exhaust fluid (DEF), is an essential component in reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions from diesel engines. Understanding its proper storage and handling ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Proper Storage Conditions for AdBlue
To preserve the quality of AdBlue, adhere to the recommended storage conditions:
- Temperature: Keep AdBlue between 10 and 25 degrees Celsius (50 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit). Extreme temperatures can degrade the fluid.
- Light Exposure: Store AdBlue in sealed containers away from direct sunlight. Exposure to ultraviolet rays can break down the solution.
- Humidity: Maintain storage areas at an appropriate humidity level. Excessive moisture can contaminate the fluid.
Using High-Quality Products
The quality of AdBlue directly impacts its lifespan and effectiveness. Choose ISO-certified products that meet industry purity and concentration standards. High-quality AdBlue is free from contaminants and maintains its chemical stability for extended periods.
Tips for Extended AdBlue Lifespan
- Regular Usage: Regularly using AdBlue prevents excessive storage and ensures the fluid remains fresh.
- First-In, First-Out: Use older AdBlue before newer batches to avoid prolonged storage.
- Inspect Regularly: Periodically check AdBlue levels and the condition of the fluid. Look for discoloration, odor changes, or signs of contamination.
- Avoid Contamination: Use dedicated containers, handling equipment, and nozzles for AdBlue. Avoid mixing with other fluids or additives.
**AdBlue Lifespan Extension: The Power of Regular Usage**
When it comes to the longevity and effectiveness of AdBlue, regular usage plays a crucial role in preventing excessive storage and optimizing its performance. Let’s delve into how it works:
Preventing Excessive Storage
Excessive storage can lead to AdBlue degradation over time, compromising its ability to reduce NOx emissions effectively. Regular usage ensures that the AdBlue in your vehicle’s tank is regularly replenished, reducing the risk of extended storage and quality issues. This frequent turnover keeps the AdBlue fresh and potent for optimal performance.
Improved AdBlue Effectiveness
Regular usage not only prevents degradation but also enhances AdBlue‘s effectiveness. When the SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) system relies on fresh and high-quality AdBlue, it can effectively convert harmful NOx emissions into harmless nitrogen and water. This ensures that your vehicle meets the latest emission standards while protecting the environment.
Storytelling Example:
Imagine a hardworking diesel truck that travels long distances every day. By regularly replenishing its AdBlue tank, the truck owner ensures that the SCR system always has access to fresh and potent AdBlue. As a result, the truck operates efficiently, reducing its environmental impact and maintaining optimal performance throughout its journeys.
Regular AdBlue usage is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s proper operation, reducing emissions, protecting the environment, and extending the lifespan of your AdBlue system. Remember to replenish your AdBlue tank regularly, ensuring that your vehicle benefits from the full potential of this vital fluid for years to come.
Describe signs of AdBlue degradation (color changes, odor).
Signs of AdBlue Degradation
As AdBlue ages, it undergoes a degradation process that can impact its performance and effectiveness. One of the telltale signs of this degradation is color changes. Fresh AdBlue is typically clear or light blue in color. However, as it degrades, it may turn yellowish or, in severe cases, brownish. This change in color is due to the breakdown of the active ingredient in AdBlue, urea, and the formation of impurities.
Another indicator of AdBlue degradation is odor. Fresh AdBlue has a faint, ammonia-like odor. But as it ages, it can develop a stronger, pungent smell. This odor is caused by the presence of ammonia and other volatile compounds that are released as AdBlue breaks down.
It’s important to note that the rate of AdBlue degradation can vary depending on storage conditions, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to contaminants. To ensure optimal performance, store AdBlue properly, at cool temperatures and away from direct sunlight. Also, avoid using AdBlue that has been contaminated with other fluids, such as water or diesel fuel.
AdBlue: Maintaining Engine Health and Performance
The Role of AdBlue in Clean Emissions
AdBlue plays a crucial role in reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions from diesel engines. It reacts with these harmful pollutants, converting them into harmless nitrogen and water. This process helps vehicles meet stringent emissions regulations and protects the environment.
Consequences of Degraded AdBlue
Over time, AdBlue degrades due to temperature fluctuations, storage conditions, and contamination. Degraded AdBlue loses its effectiveness, compromising its ability to reduce NOx emissions. This degradation can lead to several issues:
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: Deteriorated AdBlue leads to incomplete combustion, resulting in higher fuel consumption.
- Engine Damage: Prolonged use of degraded AdBlue can cause engine deposits and damage components over time, affecting performance and longevity.
- Emissions Violations: Vehicles with degraded AdBlue may fail emissions tests, leading to fines and penalties.
Importance of Replacing Degraded AdBlue
Replacing degraded AdBlue is essential for several reasons:
- Protects Engine: It prevents engine damage and costly repairs.
- Maintains Fuel Efficiency: High-quality AdBlue ensures optimal combustion, improving fuel economy.
- Complies with Emissions Regulations: Regular AdBlue replacement ensures vehicles meet emissions standards and avoid legal issues.
- Optimizes Performance: Fresh AdBlue ensures smooth engine operation, reducing vibrations and noise.
Troubleshooting AdBlue Issues
If you notice any unusual signs, such as a change in AdBlue color or odor, it may indicate degradation. Address these issues promptly by following these steps:
- Check AdBlue Level: Monitor the AdBlue level gauge to ensure adequate fluid in the tank.
- Inspect AdBlue Lines and Nozzles: Look for leaks or blockages that may restrict AdBlue flow.
- Test AdBlue Quality: Use a test kit to verify AdBlue concentration and purity; degraded AdBlue may need replacement.
- Consult a Mechanic: If the issue persists, consult a qualified mechanic for further diagnosis and repairs.
Maintaining proper AdBlue quality is vital for the health and performance of diesel engines. Replacing degraded AdBlue promptly prevents engine damage, optimizes fuel efficiency, ensures emissions compliance, and enhances the overall driving experience. By following these guidelines, drivers can ensure that their vehicles operate reliably and meet environmental regulations for cleaner air and a healthier planet.
Outline troubleshooting steps to resolve common AdBlue issues.
Troubleshooting AdBlue Issues
Experiencing trouble with your vehicle’s AdBlue system? Don’t fret! Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you identify and resolve common AdBlue issues:
-
Monitor Warning Lights: Pay attention to any warning lights on your dashboard that indicate an AdBlue-related issue. Ignoring these signals can lead to engine damage.
-
Check AdBlue Levels: A simple check can prevent major headaches. Regular monitoring of AdBlue levels ensures you don’t run dry, which can lead to engine shutdown and expensive repairs.
-
Use High-Quality AdBlue: Not all AdBlue is created equal. Stick to certified products that meet industry standards (ISO 22241). Impurities and contaminants can compromise your AdBlue’s effectiveness and damage the system.
-
Address Freezing: AdBlue can freeze in cold weather, rendering it unusable. Park your vehicle in a warm place or use a heater to thaw the solution. Avoid diluting AdBlue with water, as this can affect its chemical composition.
-
Clean Sensors: Faulty sensors can trigger false AdBlue warnings. Clean the sensors regularly to ensure accurate readings and prevent unnecessary system shutdowns.
-
Check for Leaks: Any visible leaks in the AdBlue system can lead to fluid loss and reduced efficiency. Inspect the tank, lines, and nozzles regularly for signs of damage.
-
Regular System Maintenance: Regular servicing and fluid changes can keep your AdBlue system running smoothly. Follow the recommended maintenance schedule provided by your vehicle’s manufacturer.
Remember, neglecting AdBlue issues can result in costly engine repairs and reduced vehicle performance. By following these troubleshooting steps and maintaining a proactive approach, you can keep your vehicle running at its best while protecting the environment.