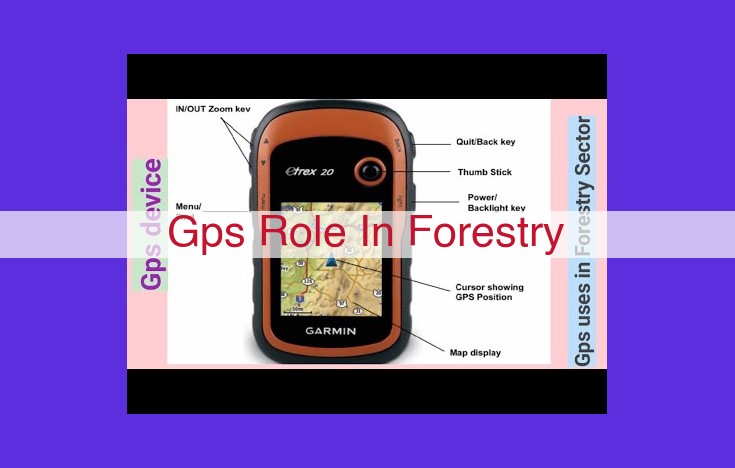
Gps Technology Revolutionizing Forestry: Accuracy, Mapping, And Beyond
GPS plays a vital role in forestry by enabling accurate measurement and mapping of forest resources, integrating with GIS for spatial analysis, providing ground-truthing data for remote sensing, facilitating precision forestry practices, and assisting in monitoring forest changes, conservation efforts, wildlife management, and carbon sequestration.
GPS in Forest Inventory: Unlocking Sustainable Forest Management
For centuries, foresters have relied on manual methods to measure and map forest resources. However, the advent of Global Positioning Systems (GPS) has revolutionized this process, enabling us to create detailed forest inventories with unparalleled accuracy and efficiency.
GPS is essentially a tool that utilizes a network of satellites to determine the precise location of a receiver on the ground. By combining GPS data with specialized software, foresters can map tree locations, measure tree heights, and estimate timber volumes with remarkable precision. This information forms the cornerstone of sustainable forest management, as it allows us to make informed decisions about forest health, timber harvesting, and conservation efforts.
One of the key advantages of GPS in forest inventory is its vastly improved accuracy compared to traditional methods. GPS receivers can determine a tree’s location within a few centimeters, while older methods could result in significant errors. This precision is crucial for creating accurate forest maps and deriving reliable estimates of timber volume.
Moreover, GPS data can be easily integrated into Geographic Information Systems (GIS). GIS software allows foresters to visualize and analyze spatial data, enabling them to identify areas with high timber value, assess forest health, and plan for future management activities.
By utilizing GPS in forest inventory, we can create detailed records of our forest resources, ensuring that we manage them sustainably for generations to come.
GPS and Remote Sensing: A Synergistic Partnership for Accurate Forest Mapping
In the realm of forest management, GPS and remote sensing technologies have forged a powerful alliance, revolutionizing the way we map and monitor forest resources. GPS (Global Positioning System) serves as the backbone for precise ground-truthing, providing vital data to calibrate and enhance the accuracy of remote sensing techniques.
Remote sensing involves capturing data about the Earth’s surface from aerial or satellite platforms. While these technologies provide valuable information about forest cover, their accuracy can be limited by factors such as cloud cover, atmospheric conditions, and sensor resolution. By incorporating ground-based measurements from GPS, we can overcome these challenges and create more accurate and reliable forest cover maps.
GPS receivers, deployed in the field, collect precise location data and attribute information about forest stands. This ground-truth data serves as a reference point for remote sensing imagery, allowing analysts to calibrate sensor readings and refine the accuracy of derived forest maps. For example, GPS can be used to validate the boundaries of different forest types, ensuring that the mapped forest cover corresponds directly to on-the-ground conditions.
The integration of GPS and remote sensing enables the creation of detailed and comprehensive forest inventories. These inventories provide forest managers with critical information about species composition, tree height, and canopy density. This data is essential for sustainable forest management, allowing for informed decisions on timber harvesting, reforestation, and conservation strategies.
By leveraging the combined strengths of GPS and remote sensing, we can create highly accurate forest cover maps that support a wide range of applications. These include:
- Identifying and monitoring areas of forest disturbance, such as deforestation and wildfires
- Estimating forest biomass and carbon stocks
- Predicting forest growth and yield
- Planning and managing forest roads and trails
- Assessing wildlife habitat and identifying protected areas
The synergy between GPS and remote sensing has revolutionized how we map and monitor forest resources, providing a powerful tool for sustainable forest management and conservation.
GPS in Precision Forestry: Empowering Data-Driven Forest Management
In the world of forestry, GPS (Global Positioning System) has emerged as a transformative tool, revolutionizing how we manage and optimize our forest resources. Precision forestry, made possible by the integration of GPS technology, has opened doors to new possibilities in forest management.
With GPS, foresters can now access precise locational data, enabling them to create detailed maps that accurately depict forest resources. This empowers them to implement variable-rate treatments, tailoring management practices to specific areas within a stand. By applying herbicides or fertilizers at targeted rates, foresters can optimize yields while minimizing environmental impact.
Furthermore, GPS allows for the establishment of precise management zones, dividing forests into distinct units based on characteristics such as tree species, soil type, and slope. By managing each zone according to its unique attributes, foresters can enhance growth, improve timber quality, and promote overall forest health.
The benefits of GPS in precision forestry extend far beyond data collection. This technology also facilitates resource optimization, enabling foresters to make informed decisions about resource allocation. By identifying areas of high productivity and low accessibility, they can prioritize harvesting operations, minimizing costs and maximizing returns.
In essence, GPS has transformed precision forestry into a powerful tool that empowers foresters to manage forests more efficiently and sustainably. Through precise data collection, targeted treatments, and optimized resource allocation, GPS plays a vital role in ensuring the preservation and prosperity of our precious forest ecosystems.
GPS and GIS: A Powerful Duo for Forest Management
In the realm of forest management, the integration of GPS (Global Positioning System) and GIS (Geographic Information System) has revolutionized the way data is collected, analyzed, and visualized. This dynamic partnership empowers foresters with the tools they need to make informed decisions and ensure the sustainable management of our precious forests.
GPS Technology: Precision Mapping for Forest Inventories
GPS technology has become an indispensable tool for creating detailed and accurate forest inventories. By precisely measuring the location of trees, soil samples, and other forest resources, GPS enables foresters to map and quantify these assets, providing a comprehensive picture of the forest ecosystem. This data forms the foundation for sustainable management practices, ensuring that forests are harvested responsibly and that biodiversity is preserved.
GIS: Visualizing and Analyzing Forest Information
GIS software provides a powerful platform for visualizing and analyzing the spatial data collected through GPS. It allows foresters to create interactive maps that depict the location and distribution of forest resources, as well as other relevant information such as soil types, topography, and land ownership. By overlaying different layers of data, GIS helps foresters identify patterns, trends, and relationships that would otherwise remain hidden.
The GPS-GIS Synergy: Empowering Forest Management
The integration of GPS and GIS creates a synergistic effect that amplifies the capabilities of both technologies. GPS provides accurate and reliable spatial data, while GIS transforms this data into visual representations that are easy to interpret. Together, they enable foresters to:
- Plan Timber Harvests: GPS-GIS data aids in identifying the most suitable areas for harvesting, considering factors such as tree density, slope, and proximity to infrastructure.
- Design Road Networks: GIS maps help plan efficient road networks that minimize environmental impact and optimize access to forest resources.
- Monitor Forest Health: By tracking changes in forest cover and vegetation over time, GPS-GIS data provides insights into forest health and allows for early detection of disturbances such as wildfires and insect infestations.
- Identify Critical Habitats: GIS maps help identify sensitive habitats and protected areas, ensuring that conservation efforts are targeted effectively.
- Support Wildlife Management: GPS-GIS data enables the tracking of animal movements, the identification of important habitats, and the monitoring of wildlife populations for effective management.
The integration of GPS and GIS has transformed forest management practices, providing foresters with unprecedented access to spatial data. By visualizing and analyzing this data, they can make informed decisions that ensure the sustainable management of our forests, preserving their ecological integrity and economic value for generations to come.
GPS: A Vital Tool for Forest Monitoring
In the realm of forest management and conservation, Global Positioning System (GPS) technology has emerged as a critical tool for tracking forest changes, monitoring disturbances, and providing real-time data that empowers conservation efforts.
GPS plays a pivotal role in aiding foresters and ecologists in understanding the dynamics of forest ecosystems. By accurately locating and mapping forest features, GPS devices provide essential information for assessing changes in forest cover, species composition, and structural complexity. The resulting data allows experts to identify areas of concern, such as deforestation, fragmentation, and habitat loss, enabling timely interventions to preserve and protect our valuable forest resources.
Moreover, GPS enables continuous monitoring of forest disturbances caused by natural events like wildfires, insect outbreaks, or storms. By providing precise coordinates and timestamps of these events, GPS facilitates rapid response and damage assessment, paving the way for effective reforestation and restoration efforts.
Empowering conservationists with real-time data, GPS enhances their ability to detect and address emerging threats. GPS-equipped field teams can track animal movements, monitor wildlife populations, and identify critical habitats. This information forms the basis for informed decision-making and targeted conservation measures aimed at safeguarding biodiversity and ecosystem integrity. By providing a holistic overview of forest conditions, GPS contributes significantly to the development of sustainable forest management practices that balance economic, social, and environmental considerations.
GPS in Forest Planning: A Precision Tool for Sustainable Management
Forests, the lungs of our planet, play a crucial role in the global ecosystem. Managing these vast ecosystems requires meticulous planning, and GPS (Global Positioning System) has emerged as an indispensable tool in this endeavor.
Precision planning with GPS ensures accurate timber harvests, road networks, and other essential management activities. With GPS, forest managers can precisely locate and map forest resources, designate specific areas, and plan operations with optimal efficiency. This reduces waste, minimizes environmental impact, and maximizes the sustainability of forest ecosystems.
For instance, GPS-guided timber harvests allow managers to identify and target trees with precision. This minimizes damage to surrounding vegetation, preserves forest ecosystems, and optimizes timber yield. Similarly, GPS-assisted road network planning ensures that roads are efficiently located and constructed, minimizing habitat fragmentation and protecting sensitive areas.
Moreover, GPS facilitates the integration of spatial data from different sources into GIS (Geographic Information System) platforms. This enables forest planners to visualize and analyze data from terrain maps, satellite imagery, forest inventories, and other sources. This comprehensive view empowers them to make informed decisions and plan for the long-term sustainability of forest resources.
In summary, GPS is a transformative tool in forest planning. Its precise location data and spatial data integration capabilities enhance efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and promote sustainable management practices. With GPS, forest managers can plan for the future of our precious forest ecosystems, ensuring their health and productivity for generations to come.
GPS in Forest Conservation: A Guardian of Nature’s Treasures
In the vast tapestry of forest ecosystems, GPS (Global Positioning System) plays a crucial role as a steadfast companion to conservationists. This invaluable technology empowers us to precisely identify and safeguard delicate habitats, protected areas, and imperiled species.
With GPS at our disposal, we can pinpoint the exact locations of pristine wetlands, lush riparian zones, ancient growth forests, and other areas of high ecological value. This detailed spatial data allows us to create comprehensive maps that guide conservation planning, land use decisions, and habitat protection measures.
Moreover, GPS provides invaluable support in monitoring threatened and endangered species. By tracking the movements of elusive animals like jaguars or sea turtles, scientists can identify critical habitats and migratory corridors, enabling targeted conservation efforts. GPS also facilitates population surveys, ensuring that species are thriving and their numbers remain stable.
By empowering us with precise location data, GPS empowers conservationists to make informed decisions, protect vulnerable ecosystems, and safeguard the integrity of our natural heritage for generations to come.
GPS in Wildlife Management
- Discuss how GPS assists in tracking animal movements, identifying habitats, and monitoring wildlife populations for management purposes.
GPS in Wildlife Management: Tracking the Trails of Nature’s Wonders
In the vast tapestry of nature’s realm, wildlife roams free, their existence intertwining with the delicate balance of their surroundings. To understand and protect these enigmatic creatures, wildlife managers rely on a powerful tool: the Global Positioning System (GPS).
Unveiling Animal Movements
GPS collars, fitted on wildlife, provide an unprecedented window into their secretive lives. By tracking their every step, scientists unravel the intricate patterns of their migrations, daily routines, and home ranges. This information is crucial for understanding population dynamics, habitat requirements, and potential conflicts with human activities.
Identifying Keystone Habitats
The data gathered from GPS tracking helps identify critical habitats—areas that are essential for wildlife survival and reproduction. By overlaying movement patterns on geographic maps, managers can pinpoint areas of high use, such as feeding grounds, nesting sites, and travel corridors. This knowledge is vital for conservation efforts, ensuring that these vital spaces are protected from encroachment and degradation.
Monitoring Population Trends
GPS collars transmit regular location updates, allowing researchers to track wildlife populations over time. By analyzing these data, they can assess population trends, estimate abundance, and detect changes in distribution. This information forms the foundation for evidence-based management decisions, such as setting hunting regulations, implementing conservation programs, and mitigating human-wildlife conflicts.
GPS technology has revolutionized wildlife management, providing invaluable insights into the secretive world of animals. By tracking their movements, identifying their habitats, and monitoring their populations, GPS empowers managers to make informed decisions that ensure the preservation of these precious creatures and their delicate ecosystems.
GPS Transforms Forest Management with Precision Silviculture
GPS (Global Positioning System) has revolutionized forestry, enabling unprecedented precision in managing our precious forest resources. In the realm of precision silviculture, GPS plays a pivotal role, empowering foresters with the ability to tailor treatments to the unique characteristics of each tree, optimizing growth and forest health.
Gone are the days of uniform management practices. With GPS technology, foresters can now pinpoint the exact location of each tree, accessing a wealth of data on its species, height, diameter, and health. This granular information serves as the foundation for customized treatments that cater to the specific needs of each individual tree.
By leveraging GPS data, foresters can identify trees with exceptional growth potential, targeting them for special care and attention. This targeted approach ensures that resources are directed where they will have the greatest impact, maximizing timber yields and fostering robust forest ecosystems.
Moreover, GPS enables the creation of precise management zones. By dividing the forest into smaller, homogeneous units based on GPS data, foresters can implement tailored treatments for each zone, accounting for variations in soil conditions, topography, and vegetation. This zoning approach optimizes resource allocation, ensuring that each area receives the most appropriate management strategies.
In precision silviculture, GPS is an indispensable tool that empowers foresters with the knowledge and technology to manage forests with unprecedented precision. By tailoring treatments to individual trees and implementing targeted management zones, GPS helps maximize forest productivity, enhance forest health, and ensure the sustainability of our valuable forest resources for generations to come.
GPS in Yield Mapping: Optimizing Forest Management for Economic Returns
In the realm of forestry, technology plays an indispensable role in maximizing timber production while ensuring sustainable practices. Among these advancements, GPS (Global Positioning System) stands out as a powerful tool that enables precise yield mapping, ultimately enhancing forest management for profitable returns.
Precision Estimation and Timber Volume Calculations
GPS technology empowers foresters with accurate data for timber volume estimation. By integrating GPS receivers into forest inventory processes, they can measure tree diameters, heights, and locations with exceptional precision. This detailed information feeds into advanced yield models, which generate estimates that predict the volume of timber available for harvesting.
Optimized Harvest Planning for Maximum Yields
Armed with accurate timber volume estimates, forest managers can optimize harvest plans to maximize yields while minimizing waste. GPS guides foresters to specific areas with high-quality timber, ensuring efficient extraction and minimizing environmental impact. By leveraging GPS data, harvesting operations become more targeted and cost-effective.
Precision Silvicultural Practices for Sustainable Profits
GPS also facilitates precision silvicultural practices that promote forest health and increase timber quality. By pinpointing the exact location of individual trees, forest managers can tailor treatments to specific needs. GPS-guided variable-rate application of fertilizers and herbicides ensures optimal nutrient delivery, leading to higher tree growth rates and improved timber value.
Data-Driven Decision-Making for Forest Management
The integration of GPS data into forest management systems provides valuable insights that support informed decision-making. By overlaying yield maps with GIS data, foresters can visualize timber resources in relation to other factors such as transportation networks, protected areas, and environmental constraints. This comprehensive view enables managers to choose harvest sites strategically, minimize environmental impacts, and maximize economic returns over the long term.
GPS technology has revolutionized yield mapping in forestry, enabling foresters to harness data for more precise and profitable management practices. From accurate timber volume estimation to optimized harvest planning and tailored silvicultural treatments, GPS empowers forest managers to enhance productivity, ensure sustainability, and maximize economic returns from their forestry operations. By embracing GPS technology, the forestry industry can continue to meet the growing demand for timber while safeguarding the integrity of our forest ecosystems.
GPS: A Vital Tool in Carbon Sequestration and Forest Monitoring
Forests play a crucial role in the global carbon cycle, acting as natural carbon sinks that absorb and store atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2). As concerns about climate change intensify, efforts to enhance carbon sequestration and monitor forest health have become paramount.
GPS (Global Positioning System) has emerged as an indispensable tool in these endeavors. Its precise location data enables foresters and researchers to accurately assess forest carbon stocks and track changes in forest cover over time.
1. Assessing Forest Carbon Stocks
GPS facilitates the establishment of forest inventory plots, where tree species, diameter, and height are measured. These measurements, combined with GPS coordinates, provide essential data for estimating forest biomass and carbon content. By extrapolating these estimates to larger forest areas, scientists can determine the total carbon stocks within a given region.
2. Monitoring Carbon Sequestration
GPS also plays a vital role in monitoring the dynamics of forest carbon sequestration. By periodically resurveying inventory plots, researchers can quantify changes in biomass and carbon stocks over time. This information helps evaluate the effectiveness of forest management practices, such as afforestation, reforestation, and sustainable harvesting, in sequestering carbon.
3. Tracking Forest Changes
The precise location data provided by GPS enables the detection of subtle changes in forest cover and structure. By overlaying historical and current GPS data, researchers can identify areas of deforestation, degradation, or regrowth. This information is crucial for understanding the impact of human activities and natural disturbances on forest carbon dynamics.
4. Conservation and Policy Planning
The carbon sequestration data derived from GPS is not only valuable for scientific research but also for conservation and policy planning. Identifying forests with high carbon storage potential can inform land-use decisions, such as prioritizing areas for protection and implementing carbon-friendly management practices.
5. Sustainable Forest Management
GPS-based forest inventories and carbon monitoring systems enable forest managers to tailor their practices to enhance carbon sequestration and mitigate climate change. By understanding the carbon dynamics of their forests, managers can optimize harvesting rates, implement selective logging techniques, and promote sustainable forest growth.
GPS has become an indispensable tool for assessing forest carbon stocks, monitoring carbon sequestration, and tracking forest changes. Its precise location data empowers foresters and researchers to contribute to the fight against climate change by improving forest management practices and supporting conservation efforts. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, GPS will continue to play a critical role in safeguarding our forests and ensuring their continued role as vital carbon sinks.